
BIOLOGICAL
Biology : Study of life
Natural Regulation - Biological Systems
Ecology as Science = Mechanistic
Explanation of natural phenomena
Ecosystem

Biotic Abiotic
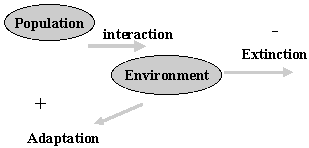
Closed system
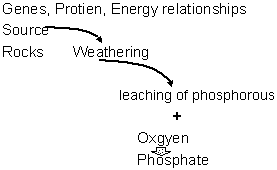
Phosphorous Energy
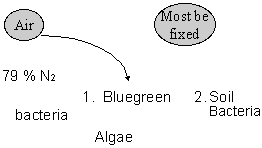
Nitrogen Succession
Human Ecology
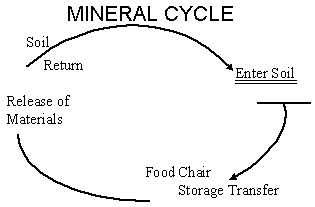
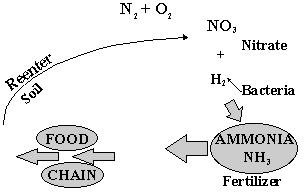
NITROGEN CYCLE (GAS)
Essential proteins genes organic chemicals
ENERGY CYCLE NOT RECYCLED IN NATURE
Law of Thermodynamics:
1. Conservation
Energy can’t be created or destroyed.
2. Entropy
Energy is always lost when used for work.
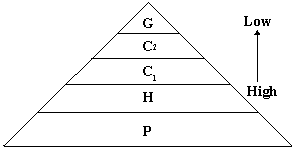
TROPIC LEVELS
Autotroph - Self Feeding - Green plants
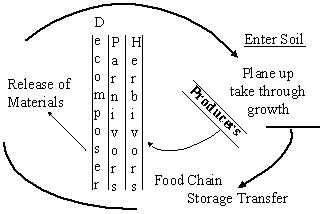
More precise than food chain.
Food relationship form a complex net or web
greater diversity is greater stability.
1. Number of organisms in a population
2. Introduction of new species
3. "Old" species become locally extinct
4 . Habitat conditions also change microclimatic.
Volcanism
lifting
Landslide
Expose new land area Ex: Bare rock succession
Dry
No soil
No shelter from exposure
1. Moss
2. Ferus
3. Grasses
4. Limital animal species
5. Shrubs
6. Trees
7. Trees
PHOTOSYNTHESIS - RESPIRATION
![]()
Enzymes are Catalyst for sugar use.
Return to the Week 2 Activities Page