 |
|||||
| |
|
|
|
|
|
ESE 625
Module Six
Assignment: FBA and BIP
Directions:
• Review the following information about the FBA, BIP and Manifest Determination process.
• Identify one youngster with whom you are working who has an FBA and/or BIP in place. Using the proper protocol and privacy requirements, access his or her file and review the documents.
• Interview the special education teacher who is working with the youngster.
• With proper permission, spend a minimum of 3 hours observing the student and documenting the current plan and its strengths and weaknesses.
• Based on your findings, develop an FBA and BIP for that youngster.
• Turn in the assignment and then once graded, place the material in your portfolio, using taskstream.
Looking out for the needs of the individual |
|
Looking out for the needs of the group |
This is a model of what the law IDEA 2004 (effective July 1, 2005) and IDEA 2004 federal regulations (effective October 13, 2006) asks us to do.

Remember, this model can be used at any time. A BIP and FBA are useful processes for thinking about behaviors that prevent a child or the classroom from effectively learning and working. They help the teacher and the student systematically improve.
If a student who meets criteria in the IDEA law as ED, the school is mandated, BY LAW, to hold a manifest determination before the student is suspended.
Manifest Determination |
|
Suspension |
The manifest determination hearing, an IEP team meeting, occurs after a child with a documented disability is recommended for suspension. An alternative educational setting (AES) may be requested. ..for certain drug and weapons offenses or inflicting serious bodily injury at school. |
Expulsion |
Before expulsion can be initiated for a student with a disability, the IEP team must conduct a "manifest determination." In this meeting they must determine whether the behavior exhibited by the student that resulted in expulsion was: 1) a result of the disability; 2) a result of the school not implementing the IEP and behavior plans adequately. The MD hearing must occur within twenty (20) school days after the decision was made to recommend an expulsion. The final decision must be made by ten (10) school days after the hearing. The law no longer states that the child continues to “stayput” |
Disagreement |
If the student's parents disagree with the manifest determination meeting decision, a due process hearing can be requested from a panel outside of the basic IEP team. This centers on the question of whether the child's disability led to the behaviors. If yes, the child cannot be expelled. If no, the school can terminate services. |
The Process
• Background Information – Look in records and ask parents, the nurse, other teachers, the child --
• The FBA piece --Is the behavior problem real? Document and establish the antecedents, the frequency, the seriousness of the problem.
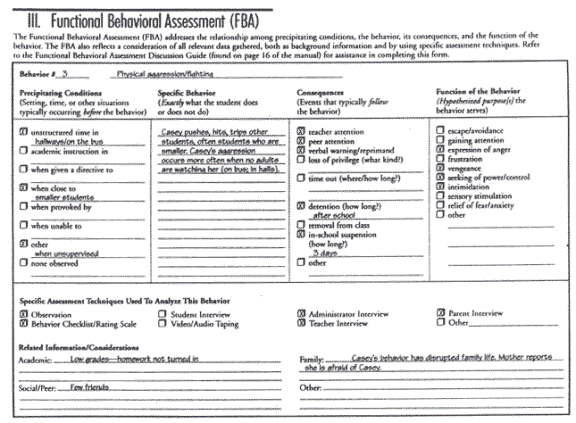
Identifying the reasons for behavior will take many forms, and while the IDEA advises an FBA approach to determine specific contributors to behavior, it does not require or suggest specific techniques or strategies to use when assessing that behavior. However, several key steps are common to most FBAs:
• Verify the seriousness of the problem.
• Define the problem behavior in concrete terms.
• Collect data on possible causes of problem behavior.
• Analyze the data.
Formulate and test a hypothesis.
3. Causal determination – Hold a meeting to get agreement about the findings.
![]() You will not do this step during the assignment, since it may be invasive. In the future, you will include this crucial part of the process.
You will not do this step during the assignment, since it may be invasive. In the future, you will include this crucial part of the process.
4. Developing the Behavioral Intervention Plan
The following is a very good link to review behavior management concepts.
http://www.ldonline.org/ld_indepth/behavior/behavioral_intervention.html
Once the FBA, observations and manifest determination steps are completed it is time for the BIP.
• Review of the behavior targeted in the functional behavioral assessment.
• Determination of behavioral goals that relate to increasing or decreasing the specific behavior.
• Determination of the specific intervention strategies appropriate for the behavior. Designation of the individual (or individuals) responsible for implementing the plan.
• Determination of the appropriate dates for review of the plan and evaluation of its success.
• Determination of the appropriate methods for evaluation of the plan. Fad (1998)
Links to excellent sample forms:
http://www.mfba.net/forms.html
http://fifa.fmhi.usf.edu/schoolforms.htm

Charts from:
Horner, R. H, O'Neill, R. E., Albin, R. W., Sprague, J. R., Storey, K., Newton, J. S. (1997) Functional assessment and program development for problem behavior: A practical handbook. Pacific Grove, CA: Brooks/Cole.
The seven step plan is used to analyze a student behavior or set of behaviors.
1. Identify the problem behavior.
2. Define the behavior clearly in observable terms.
3. Observe the student in the setting.
4. Identify antecedents for student misbehaviors
5. Look for or ask about the needs being fulfilled or the student motives.
6. Identify replacement behaviors that are likely to fulfill the student needs.
7. Develop and implement an intervention plan as a team.
Final Exam Activity: 2 |
Directions: This is the final exam for the course. Please review the major concepts and constructs that contributed to our discussions and learning activities.
Concepts about discipline were presented in various modules in the discipline
course. You may want to review how these impact the pro-active classroom.
|
|
|
Now build ten tools that will help you move your classroom into this 21st
century, empowering position. Share them with the professor and get that well
deserved A.