CHM238-01 F02 Practice Exam 1 September 18, 2002
Name: Keynote
1. Draw the following: Aniline meta-xylene p-Chloroethylbenzene
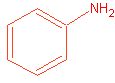
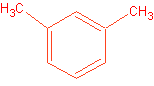
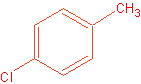
Naming will be the official exam as well.
2. Cyclopentadiene has a pKa = 15, while the usual C-H bond is pKa = 45.
(a) Write out using powers of 10 (10x) the number of times more acidic cyclopentadiene is: 1030
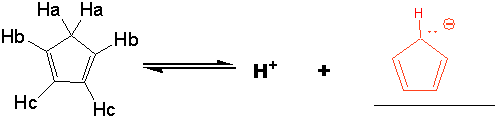
Which proton is the most acidic in cyclopentadiene and why? Make sure that you explain the stability of the anion formed in your answer.
The cyclopentadienyl anion is aromatic: 6 pi electrons, all sp2 C’s. A normal carbanion
is not stabilized.
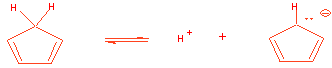
![]()
We
can write the competition reaction by adding the two:
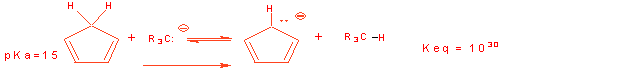
Provide the product for the following proton disassociation reaction:
(b) Given that pKa for
NH4+ = 9, pKa for H2O
= 16, and pKa for NH3 = 33,pick the appropriate base that will convert cyclopentadiene to the cyclopentadienyl
anion in overwhelming amounts. Then
write the complete reaction including the base you picked that will form the
anion in large excess: Keq = 1018
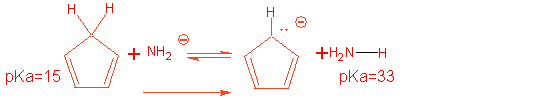
3. Draw the needed lone pairs and arrows to complete the following reaction sequence:

Answer these questions about the reaction:
a. Another product from the reaction of 1,3-butadiene and HBr is:
1,2 addition
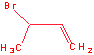
b. The above mechanism has a step that goes from a more stable species to a more unstable species. What type of cation intermediate is formed first and which cation intermediate is formed.?
20
allylic formed first and is
more stable than 10 allylic cation. The allylic cation is stable enough
to rearrange with enough heat.
c. What would the product(s) be of the reaction of 1,3-butadiene with 2 moles of HBr?
4. Predict the product of the following Diels Alder reaction:

The diene above is trans,trans-2,4-hexadiene? The cis,cis-2,4-hexadiene has the methyl groups close to each other. Why does the cis,cis isomer react with the dienophile so much slower than the trans, trans?
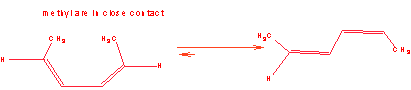
What would be the effect on the rate of the reaction if the dienophile were trans and not cis?
none cis and trans
don’t make any difference in dienophile.
Would cis-2-butene make a good dienophile? Why or why not?
No,
CH3 is an EDG. EWG activate dienophiles. EDG
activate dienes.
What would be the stereochemistry of the product of trans, trans-2,4-hesadiene + the dienophile above?
meso
Assign the NMR spectrum of the Diels Alder adduct
from above: Draw arrows from H’s to
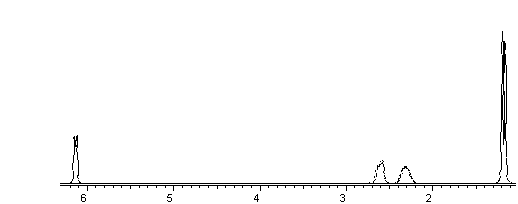
e a b d c
5. Which diene and dienophile reacted to form the following?
a)
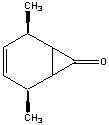
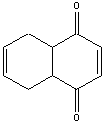 b)
b)
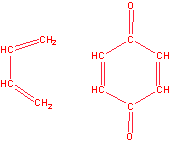
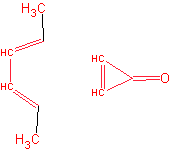
6. (a) Which of the following molecules are aromatic? Give your reasoning.
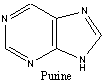
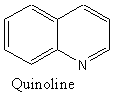
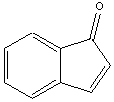
Aromatic or NA Aromatic or NA Aromatic or NA
# of pi e’s= 8 # of pi e’s= 10 # of pi e’s= 10
Reasons: Reasons: Reasons:
not 4n+2 4n+2
all sp2 4n+2
all sp2
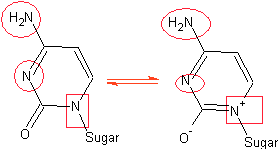
(b) For the structure of Cytosine:
1. Circle N’s could participate in H bonding?
2. Put a square around the N’s that are not basic.
3. Draw a resonance structure by pushing the LP
on an N to the carbonyl. Explain how this structure
is consistent with cytosine being aromatic.
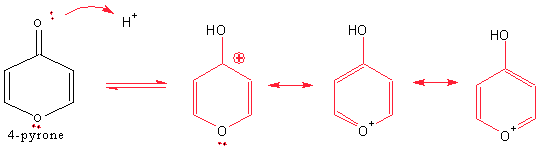
(c) 4-pyrone is protonated on the carbonyl oxygen to give a stable cationic product. Draw the structure of the protonated form of 4-pyrone and explain with a resonance structure, why the product is so stable.
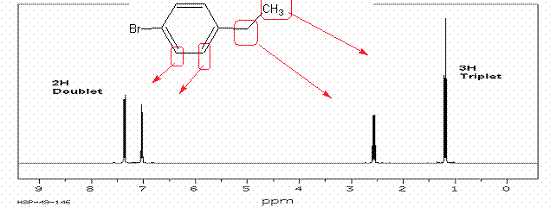
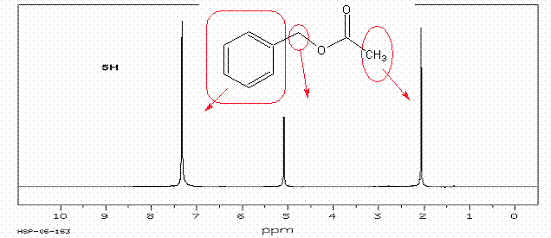
7. Draw out a structure that will fit the following HNMR
spectra. Start with calculating the
degree of unsaturation. To receive full credit, assign all HNMR peaks by drawing an arrow to
the peak from the structure. A. The
first two have the structure C9H10O2:
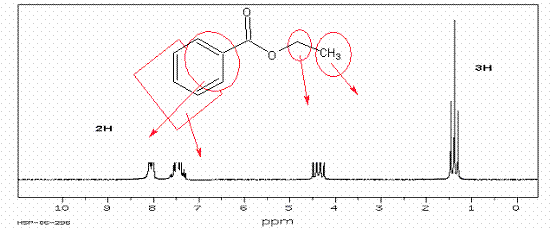
B. The formula of C8H9Br