| ESE424 : The Class : Students with Mild Disabilities : Mental Retardation : What is Mild Mental Retardation? | |||||
What is Mild Mental Retardation?
This topic is subdivided into three 3 major themes:
- Understanding Mental Retardation
- Definitions of Mental Retardation and Mild Mental Retardation
- Prevalence of Mild Mental Retardation
What is mild mental retardation?
Individuals who have mild mental retardation are part of a larger group of persons with mental retardation. As such, they share many of the same characteristics, are exposed to the same biases and misperceptions, and exhibit the same difficulties with academic learning, albeit to a lesser extent than those with more severe forms.
Before focusing on mild mental retardation exclusively, it is important to examine mental retardation as a whole. The term mental retardation is, as much as anything else, an idea. As such it is open to many different interpretations, all colored by our experiences, prejudices, and perceptions. If you were to randomly select 10 people and ask them what mental retardation is, they would probably give you an equal number of definitions - most likely none of which relate to the legal definitions we will review in a few moments. What then is "mental retardation?"
Mental retardation is probably best described as:.
Definitions of Mental Retardation and Mild Mental RetardationAs you can see, the concept of mental retardation is a slippery one. Definitions of mental retardation are no less difficult to pin down. You see, the definitions we use are a social or political phenomena. These descriptions do not rest with the person; rather, they come from others who attempt to construct these definitions. To date, there are more than 30 definitions of mental retardation. Two, however predominate. Neither of these overtly identify mild mental retardation as a discreet category. The Federal Definition of Mental Retardation (IDEA)
The American Association on Mental Retardation (AAMR)
Neither definition differentiates between mild and severe mental retardation. However, practitioners and clinicians use the following scale to make these determinations for either definition.
The American Association of Mental Retardation - Levels of SupportThe AAMR, in addition to the IQ and adaptive behavior standards uses levels of support to differentiate mild from more severe forms of mental retardation. Click on the graphic below to review these levels of support. 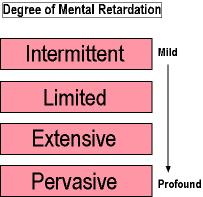
Thus, according to the AAMR definition a person in the mild range of mental retardation would be one who requires only limited support.
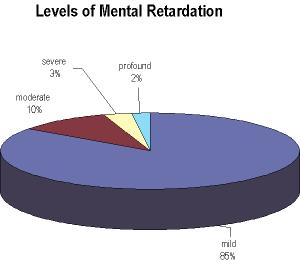
The Prevalence of Mental RetardationAccording to the most recent Annual Report to Congress on the Implementation of the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, there are 594,025 children with mental retardation attending our schools. This group constitutes the third largest category of children receiving special education services. Using the IDEA and AAMR definitions and tables, the number of children receiving special education under the diagnostic category of mental retardation, and the distribution of IQ scores, we can break down the entire population of children with mental retardation into the following distribution.
As you can see, individuals with mild mental retardation represent the preponderance of children, adolescents and adults in this category. Mild Mental Retardation.Thus, using the IDEA and AAMR definitions of mental retardation ,contemporary diagnostic practice, and current population statistics, we see that children with mild mental retardation:
However, we need to go a little further than just overall prevalence figures. You need to realize that the number of children with mild mental retardation are not equally distributed throughout our culture. The prevalence mild mental retardation varies by: Once you have completed this lesson, you should:Go on to
Activity 1: Decline in Mild Mental Retardation E-mail the instructor at
Larry.Gallagher@nau.edu Web site created by the NAU OTLE Faculty Studio Copyright 1998 Northern Arizona
University |