| BIO 190 The Class: Introduction: Lesson 1 | ||||
| BIO 190 The Class: Introduction: Lesson 1 | ||||
Before going into your lesson, open the links below and explore.
The Electronic Zoo
Scientific American On-Line
The MAD Scientist
Network
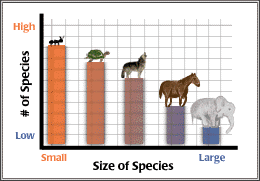
Zoology is the scientific study of animals. As you begin your study of animal biology, remember that this area of study is only a portion of biology. Biologists study life in a variety of ways, and zoologists study animals in a variety of ways. For example, zoologists are interested in the variety of species of animals and the patterns that are seen between species. One interesting pattern observed by zoologists is that there are many more species of organisms that are small in size than species of organisms that are large in size. For a graphic view of this phenomenon, look at the figure below.
Science and the Scientific Method.
Biologists, as scientists, use guiding principles to conduct their research. These principles are the standards of the scientific method. A scientist never "proves" anything, but rather gathers evidence to support or strengthen a hypothesis, or to reject a hypothesis. A scientist would not make a statement like, "There is no other explanation." A scientist would make a statement like, "Based on limited observations…"or "at this point I can only say…"
Defining Living Organisms
As scientists attempt to define life, certain common characteristics emerge that define living organisms. You have probably come up with some of your own as a result of doing the "Defining Life" assignment on the Learning on the Web page. The following are elements that biologists believe are common to all living things:
Life MUST obey certain physical laws
Life must obey the laws of thermodynamics, which describe how energy changes.
The First Law of Thermodynamics states:
Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only undergo conversion form one form to another.Darwin's theory of evolution
Chapter 9 of this course focuses on the theory of evolution. As outlined in Chapter 9, the evidence for this theory consists of:
fig. 1-17
fig. 1-18
E-mail the professor W. Sylvester Allred at Syl.Allred@NAU.EDU, or call (520)523-7214

Copyright 1997 Northern Arizona
University
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED