





 |
 |
 |
 |
  |
|
Excel- commands used in this topic (Excel in Office 97 and Office 2000)
§ Probability of x values (left tail) §
§ Probability of x values (right tail) §
§ Probability of z values (left tail) §
§ Probability of z values (right tail) §
§ x value associated with a given probability (left tail) §
§ x value associated with a given probability (right tail) §
§ z value associated with a given probability (left tail) §
§ z value associated with a given probability (right tail) §
§ Standardize § Equations §
1. Probability of x values (from left tail)
For the probability (left tail) of a range of x values in the Normal distribution: Paste Function-Statistical-Normdist (cumulative = true yields the cumulative probability; cumulative = false yields the probability mass function.)
![]()
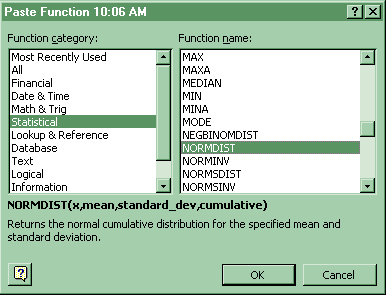
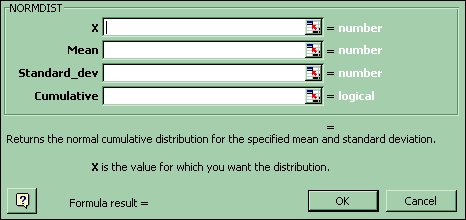
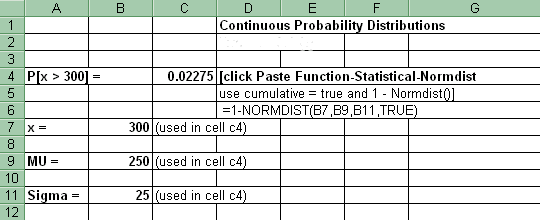
2. Probability of x values (right tail)
For the probability (right tail) of a range of x values in the Normal distribution: Paste Function-Statistical-Normdist (cumulative = true yields the cumulative probability; cumulative = false yields the probability mass function.). Then in another cell put =1 - (cell reference to Normdist). Copy and paste that formula into the cells adjacent to each x. See Probability of x values (left tail) above.
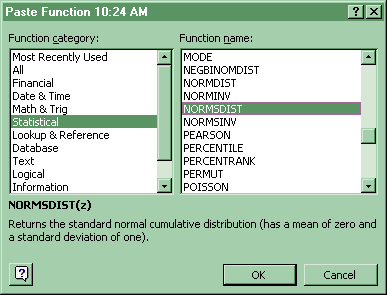
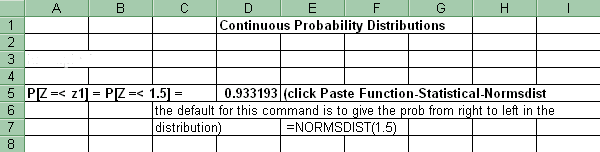
3. Probability of z values (left tail)
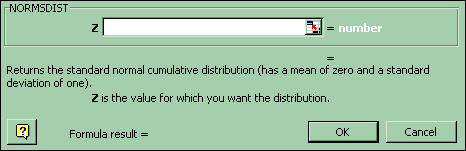
For the cumulative probability (left tail) of a range of z values in the Standard Normal distribution: Paste Function-Statistical-Normsdist. Copy and paste that formula into the cells adjacent to each Z.
![]()
4. Probability of z values (right tail)
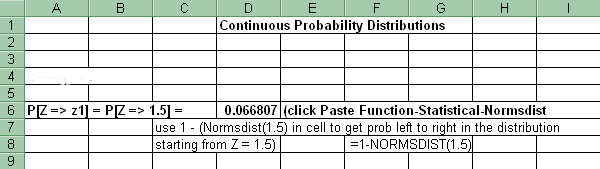
For the cumulative probability (right tail) of a range of z values in the Standard Normal distribution: Paste Function-Statistical-Normsdist. Then in another cell put =1 - (cell reference to Normsdist). Copy and paste that formula into the cells adjacent to each Z. See Probability of z values (left tail) above.
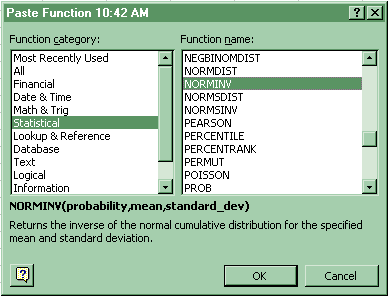
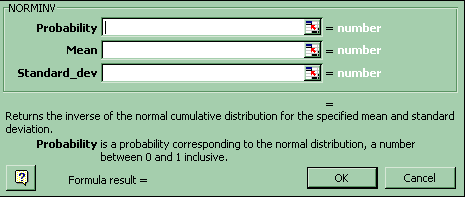
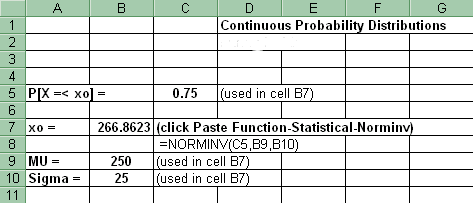
5. x value associated with a given probability (left tail)
For an x value associated with a given probability (left tail) in the Normal distribution: Paste Function-Statistical-Norminv. Copy and paste the formula into the cells adjacent to each probability.
![]()
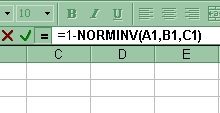
6. x value associated with a given probability (right tail)
For an x value associated with a given probability (from right to left) in the Normal distribution: Paste Function-Statistical-Norminv. Then in another cell put =1 - (cell reference to Norminv). Copy and paste that formula into the cells adjacent to each probability. See x value associated with a given probability (left tail) above. Assuming that the first probability is in A1, mean in B1 and standard deviation in C1, then the cell command would look like this:
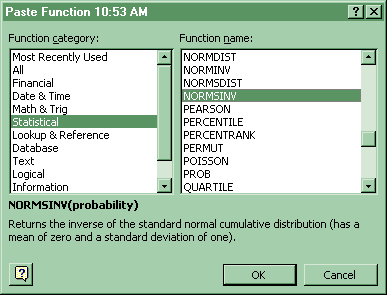
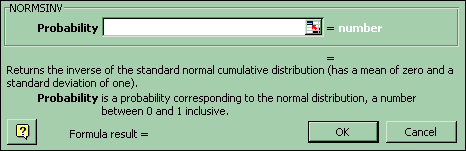
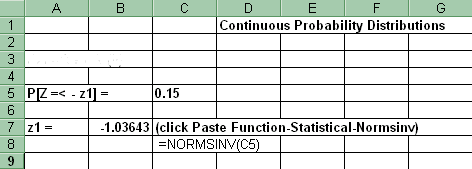
7. z value associated with a given probability (left tail)
For a z value associated with a given probability (left tail) in the Standard Normal distribution: Paste Function-Statistical-Normsinv. Copy and paste that formula into the cells adjacent to each probability.
![]()
8. z value associated with a given probability (right tail)
For a z value associated with a given probability (right tail) in the Standard Normal distribution: Paste Function-Statistical-Normsinv. Then in another cell put =1 - (cell reference to Normsinv). Copy and paste that formula into the cells adjacent to each probability. See z value associated with a given probability (left tail) above. Assuming that the first probability is in A1, then the cell command would look like this:

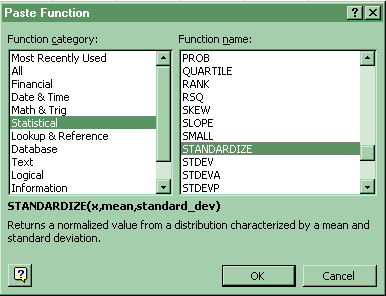
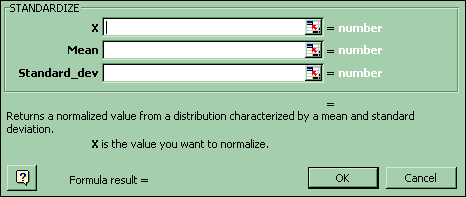
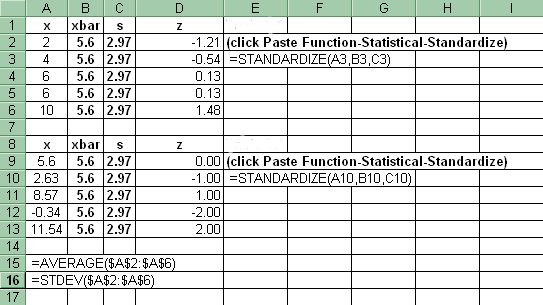
9. Standardize
To standardize an x value: Paste Function-Statistical-Standardize.
![]()
Continuous Probability
Equations
§ Z Score §
§ Equations not used at this topic site §
Equations used at this topic site
Z Score
1. Zo = [xo - m] / s
where
Zo = Z score
xo = data value
m = population mean
s = population standard deviation
Equations not used at this topic site
Normal Approximation to Binomial
1. Use the normal approximation to the binomial if np > 5 and n(1 - p) > 5 and use m = np and s = Ö( np[1 - p] ) to calculate Z.
(a) If "equal to or less than" (£) in binomial probability statement, add 0.5 units to x before doing the normal calculation.
(b) If "equal to or greater than" (³) in binomial probability statement, subtract 0.5 units to x before doing the normal calculation.
Go on to
Home Work
or
Go back to Continuous
Distributions: Activities and Assignments
Please reference "BA501 (your last name) Assignment name and number" in the subject line of either below.
E-mail Dr. James V. Pinto at
BA501@mail.cba.nau.edu
or call (928) 523-7356. Use WebMail for attachments.

Copyright 2002 Northern
Arizona University
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED