Introduction
The MPI_Scatter primitive is sends chunks of data stored in an array to several process ranks, where each rank receives different data elements. It is similar to MPI_Broadcast, except that MPI_Broadcast sends the same data to process ranks.
The syntax is as follows:
int MPI_Scatter(const void *sendbuf,
int sendcount,
MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void *recvbuf,
int recvcount,
MPI_Datatype recvtype,
int root,
MPI_Comm comm)
The MPI_Gather primitive receives data at the root from other processes. The syntax is as follows:
int MPI_Gather(const void *sendbuf,
int sendcount,
MPI_Datatype sendtype,
void *recvbuf,
int recvcount,
MPI_Datatype recvtype,
int root,
MPI_Comm comm)
Connection to Modules
- This module may be useful for the distance matrix and K-means modules.
Files Required
Sum of an Array Part 1: Implementing Scatter and Gather using Send and Recv
In this exercise, rank 0 will generate an array of size N. There are p process ranks. We assume N mod p=0, i.e., N/p divides evenly.
We will compute the total sum of the values in the array of size N using the p ranks. Using MPI_Send you will send chunks of size N/p to each process rank from rank 0. Each rank will add the values in the array together (N/p elements) and will send the data back to rank 0 using MPI_Send. At the end, rank 0 will add all of the values from each of the ranks together and output the total sum.
In this exercise, we will only use MPI_Send and MPI_Recv.
To get started, use the file scatter_starter.c.
Figure 1 shows an example of the sending the data, where N=12 and p=4. Each rank is sent N/p=3 elements to compute the local sums.
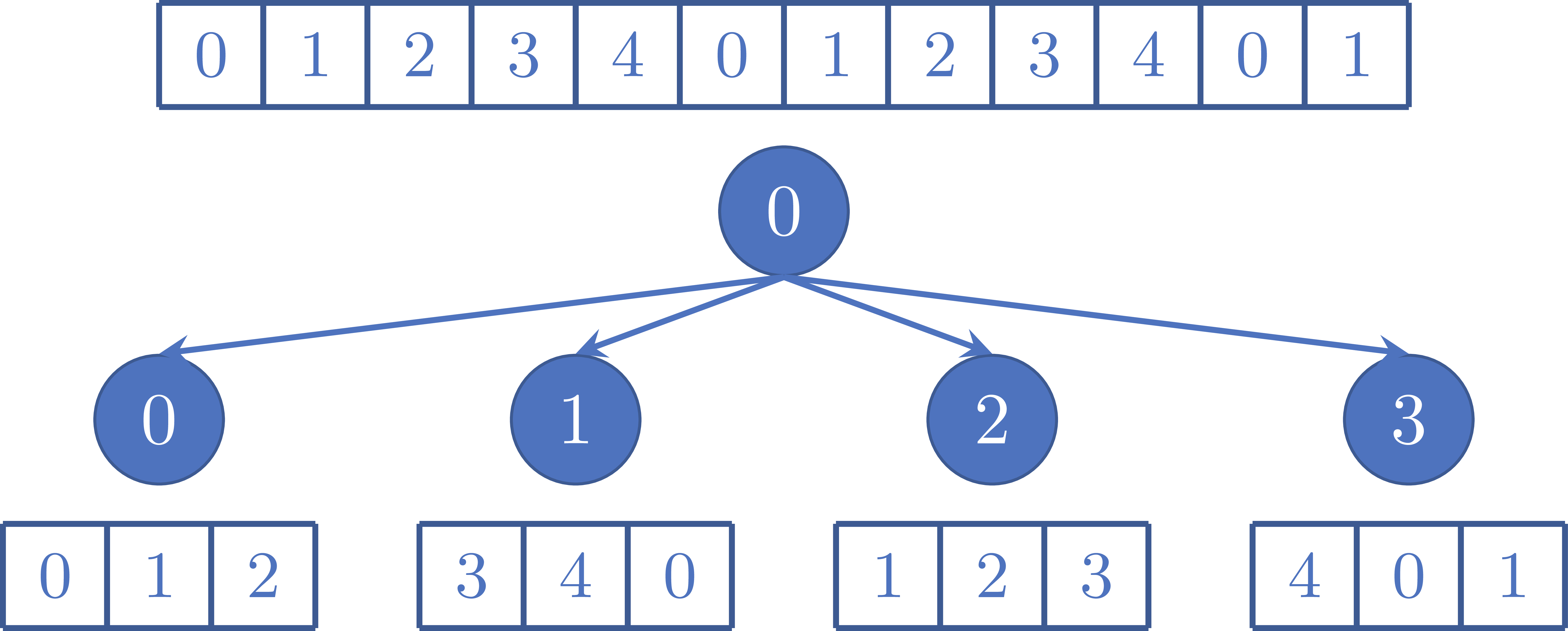
Figure 1: Example of sending chunks of size N/p=3 to p=4 ranks, where N=12.
Figure 2 shows an example of sending the data from each rank to rank 0.
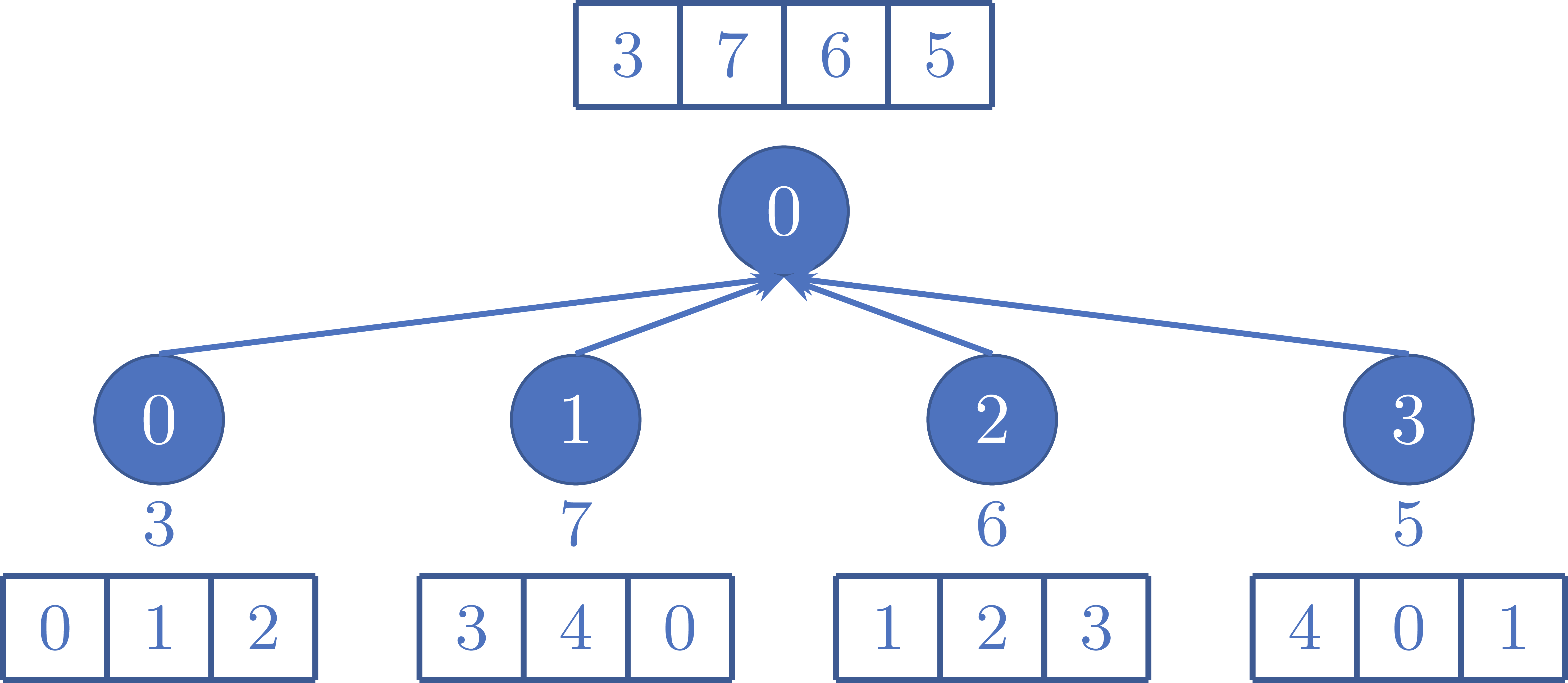
Figure 2: Example of sending the local sums of the arrays at each rank to rank 0.
Sum of an Array Part 2: Using Scatter and Gather
Copy your code from Part 1. This time, implement the program using MPI_Scatter and MPI_Gather without using MPI_Send or MPI_Recv.